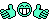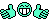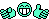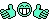
Die Sockel
Typ: Lidded Micro Pin Grid Array Package (1.27mm Pitch, 31×31 pins, 40×40mm, Organic Substrate)
Retention Modul
Die Chipsätze
Allgemeines
- der Funktionsumfang entspricht einer traditionellen Southbridge
- Marketing Name: Fusion Controller Hub (kurz FCH)
- die Anbindung an den Prozessor erfolgt per Unified Media Interface (UMI), dies entspricht 4 PCIe 2.0 Lanes mit einer Bandbreite von 2 GB/s
Chipsatz A85X A75 A55 A88X A78 A68H A58 Familie(-Modell) Hudson-D4 Hudson-D3 Hudson-D2 Bolton-D4 Bolton-D3 Bolton-D2H Bolton-D2 Sockel FM2 FM1/FM2 FM1/FM2 FM2+ FM2+ FM2+ FM2+ PCI / Express 4x PCIe 2.0 GPP
PCI (33Mhz)4x PCIe 2.0 GPP
PCI (33Mhz)4x PCIe 2.0 GPP
PCI (33Mhz)4x PCIe 2.0 GPP
PCI (33Mhz)4x PCIe 2.0 GPP
PCI (33Mhz)4x PCIe 2.0 GPP
PCI (33Mhz)4x PCIe 2.0 GPP
PCI (33Mhz)SATA (davon III) 8 (8) 6 (6) 6 (0) 8 (8) 6 (6) 4 (4) 6 (0) RAID Level 0, 1, 5, 10 0, 1, 10 0, 1, 10 0, 1, 5, 10 0, 1, 10 0, 1, 10 0, 1, 10 RAID-TREIBER Promise Promise Promise Dot Hill Dot Hill Dot Hill Dot Hill USB (davon 3.0) 14 (4) 14 (4) 14 (0) 14 (4) 14 (4) 10 (2) 14 (0) TDP 7.8W 7.8W 7.6W 7.8W 7.8W 7.8W 7.6W
Zusätzlich gibt es auch noch Embedded und Mobile-Varianten. Im Desktop-Bereich relevant ist davon nur der A70M (Hudson-M3), den Biostar auf einigen µATX Modellen verbaut hat.
Eine Liste aller Fusion Controller Hubs @ Wikipedia:

List of AMD chipsets - Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org
Die Plattformen
Ausrichtung: Mainstream-Desktop / Entry-Gaming
Llano Trinity Richland Kaveri Godavari Carrizo Markteinführung 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Microarch K10 Piledriver Piledriver Steamroller Steamroller Excavator max CPU-Kerne (Threads) 4 (4) 2 (4) 2 (4) 2 (4) 2 (4) 2 (4) GPU HD 6000D HD 7000D HD 8000D R5/R7 R5/R7 R5/R7 GPU Arch VLIW5 VLIW4 VLIW4 GCN 1.1 GCN 1.1 GCN 1.2 GPU Kerne/Shader (max) 400 384 384 512 512 512 Video De/Encode UVD 3.0 UVD 3.0 & VCE 1.0 UVD 3.0 & VCE 1.0 UVD 4.0 & VCE 2.0 UVD 4.0 & VCE 2.0 UVD 6.0 & VCE 3.1 L2 Cache (max) 4 x 1MB 2 x 2 MB 2 x 2 MB 2 x 2 MB 2 x 2 MB 2 x 1MB Arbeitsspeicher (max) DDR3-1866 DDR3-1866 DDR3-2133 DDR3-2133 DDR3-2133 DDR3-2400 TDP 65W/100W 65W/100W 65W/100W 65W/95W 65W/95W 35W/65W
1) FM1 "Lynx"
Fertigung: 32nm HKMG SOI @ GF (32SHP)
Typ: APU
Architektur "Stars"
- CPU: K10, Family 12h "Husky"
- GPU: HD 6000D, TeraScale 2 "Sumo" (VLIW5), UVD 3.0
Speichercontroller: Dual Channel DDR3, bis DDR3-1866
CPU-PCIe: PCIe 2.0
Chipsatz-Anbindung: 4x PCIe 2.0 (UMI)
Hardwareluxx-Test:
Test: AMD Llano und die Lynx-Plattform - APUs für alle - Hardwareluxx
Hardwareluxx gibt einen Vorgeschmack auf AMDs neue APU Generation Llano, doe erstmalig eine ausreichend leistungsfähige GPU in eine CPU integriert.www.hardwareluxx.de
Modellnummer CPU-Kerne Takt (max. Turbo) L2-Cache Multi (OC) Vcore GPU-Modell GPU-Konfiguration
SP (SE/TE/ROP)GPU-Takt TDP Turbo Core Marktstart RAM Sempron X2-198 2 2,5 GHz 2× 512kB 25× N/A deaktiviert 65 W Nein Q1/2012 DDR3-1600 Athlon X2-221 2 2,8 GHz 2× 512kB 28× N/A deaktiviert 65 W Nein Q1/2012 DDR3-1600 Athlon X4-631 (65W) 4 2,6 GHz 4× 1MB 26× N/A deaktiviert 65 W Nein 2012 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4-631 (100W) 4 2,6 GHz 4× 1MB 26× N/A deaktiviert 100 W Nein 8/2011 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4-638 4 2,7 GHz 4× 1MB 27× N/A deaktiviert 65 W Nein 2/2012 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4-641 4 2,8 GHz 4× 1MB 28× N/A deaktiviert 100 W Nein 2/2012 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4-651 4 3,0 GHz 4× 1MB 30× N/A deaktiviert 100 W Nein 11/2011 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4-651K 4 3,0 GHz 4× 1MB 30× (offen) N/A deaktiviert 100 W Nein 2/2012 DDR3-1866 E2-3200 2 2,4 GHz 2× 512kB 24× N/A HD 6370D 160 (32x5D-VLIW/8/4) 444 MHz 65 W Nein Q3/2011 DDR3-1600 A4-3300 2 2,5 GHz 2× 512kB 25× N/A HD 6410D 160 (32x5D-VLIW/8/4) 444 MHz 65 W Nein Q3/2011 DDR3-1600 A4-3400 2 2,7 GHz 2× 512kB 27× N/A HD 6410D 160 (32x5D-VLIW/8/4) 600 MHz 65 W Nein Q3/2011 DDR3-1600 A4-3420 2 2,8 GHz 2× 512kB 28× N/A HD 6410D 160 (32x5D-VLIW/8/4) 600 MHz 65 W Nein Q4/2011 DDR3-1600 A6-3500 3 2,1 (2,4) GHz 3× 1MB 21× N/A HD 6530D 320 (64x5D-VLIW/16/8) 444 MHz 65 W Ja Q3/2011 DDR3-1866 A6-3600 4 2,1 (2,4) GHz 4× 1MB 21× N/A HD 6530D 320 (64x5D-VLIW/16/8) 444 MHz 65 W Ja Q3/2011 DDR3-1866 A6-3620 4 2,2 (2,5) GHz 4× 1MB 22× N/A HD 6530D 320 (64x5D-VLIW/16/8) 444 MHz 65 W Ja Q4/2011 DDR3-1866 A6-3650 4 2,6 GHz 4× 1MB 26× 1,4125 V HD 6530D 320 (64x5D-VLIW/16/8) 444 MHz 100 W Nein Q3/2011 DDR3-1866 A6-3670K 4 2,7 GHz 4× 1MB 27× (offen) N/A HD 6530D 320 (64x5D-VLIW/16/8) 444 MHz 100 W Nein Q4/2011 DDR3-1866 A8-3800 4 2,4 (2,7) GHz 4× 1MB 24× N/A HD 6550D 400 (80x5D-VLIW/20/8) 600 MHz 65 W Ja Q3/2011 DDR3-1866 A8-3820 4 2,5 (2,8) GHz 4× 1MB 25× N/A HD 6550D 400 (80x5D-VLIW/20/8) 600 MHz 65 W Ja Q4/2011 DDR3-1866 A8-3850 4 2,9 GHz 4× 1MB 29× 1,4125 V HD 6550D 400 (80x5D-VLIW/20/8) 600 MHz 100 W Nein Q3/2011 DDR3-1866 A8-3870K 4 3,0 GHz 4× 1MB 30× (offen) 1,4125 V HD 6550D 400 (80x5D-VLIW/20/8) 600 MHz 100 W Nein Q4/2011 DDR3-1866
Chipätze: Hudson (A55, A75)
2) FM2 "Virgo"
Fertigung: 32nm HKMG SOI @ GF (32SHP)
Typ: APU
Architektur
- CPU: Piledriver, Family 15h (10h-1Fh)
- GPU: HD 7000D, TeraScale 3 "Devastator" (VLIW4), UVD 3.0, VCE 1.0
Speichercontroller: Dual Channel DDR3, bis DDR3-1866, unlocked bis DDR3-2400
CPU-PCIe: 24x PCIe 2.0 (davon 4 für den Chipsatz reserviert)
Chipsatz-Anbindung: 4x PCIe 2.0 (UMI)
Es gab kein Hardwareluxx Review zum Launch, aber später einige Mainboard Tests:
- ASRock FM2A85X Extreme6
- Gigabyte F2A85X-UP4 & mein User Review im Sammelthread
- Sapphire Pure Platinum A85XT
CPU Modell Modules (Threads) CPU-Takt (Turbo) L2 Cache GPU Modell SP (SE/TE/ROPs) GPU-Takt TDP Marktstart RAM Sempron X2 240 1 (2) 2,9 (3,3) GHz 1× 1MB deaktiviert 65 W DDR3-1600 Athlon X2 340 1 (2) 3,2 (3,6) GHz 1× 1MB deaktiviert 65 W Q4/2012 DDR3-1600 Athlon X4 730 2 (4) 2,8 (3,2) GHz 2× 2MB deaktiviert 65 W Q4/2012 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4 740 2 (4) 3,2 (3,7) GHz 2× 2MB deaktiviert 65 W Q4/2012 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4 750K 2 (4) 3,4 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB deaktiviert 100 W Q4/2012 DDR3-1866 A4-5300 1 (2) 3,4 (3,6) GHz 1× 1MB HD 7480D 128 (32x4D/8/8) 724 MHz 65 W Q3/2012 DDR3-1600 A4-5300B 1 (2) 3,4 (3,6) GHz 1× 1MB HD 7480D 128 (32x4D/8/8) 724 MHz 65 W Q3/2012 (OEM) DDR3-1600 A6-5400B 1 (2) 3,6 (3,8) GHz 1× 1MB HD 7540D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 760 MHz 65 W Q3/2012 (OEM) DDR3-1866 A6-5400K 1 (2) 3,6 (3,8) GHz 1× 1MB HD 7540D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 760 MHz 65 W Q3/2012 DDR3-1866 A6-6420K 1 (2) 4,0 (4,2) GHz 1× 1MB HD 8470D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 800 MHz 65 W Q1/2014 DDR3-1866 A8-5500 2 (4) 3,2 (3,7) GHz 2× 2MB HD 7560D 256 (64x4D/16/8) 760 MHz 65 W Q3/2012 DDR3-1866 A8-5500B 2 (4) 3,2 (3,7) GHz 2× 2MB HD 7560D 256 (64x4D/16/8) 760 MHz 65 W Q3/2012 (OEM) DDR3-1866 A8-5600K 2 (4) 3,6 (3,9) GHz 2× 2MB HD 7560D 256 (64x4D/16/8) 760 MHz 100 W Q3/2012 DDR3-1866 A10-5700 2 (4) 3,4 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB HD 7660D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 760 MHz 65 W Q3/2012 DDR3-1866 FirePro A300 2 (4) 3,4 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB FirePro 384 (96x4D/24/8) 760 MHz 65 W 8/2012 (OEM) DDR3-1866 A10-5800B 2 (4) 3,8 (4,2) GHz 2× 2MB HD 7660D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 800 MHz 100 W Q3/2012 (OEM) DDR3-1866 FirePro A320 2 (4) 3,8 (4,2) GHz 2× 2MB FirePro 384 (96x4D/24/8) 800 MHz 100 W 8/2012 (OEM) DDR3-1866 A10-5800K 2 (4) 3,8 (4,2) GHz 2× 2MB HD 7660D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 800 MHz 100 W Q3/2012 DDR3-1866
Chipsätze:
- FM2: Hudson (A45, A55, A75, A85X)
- FM2+: Bolton (A58, A68H, A70M, A78, A88X)Fertigung: 32nm HKMG SOI @ GF (32SHP)
Typ: APU
Architektur
- CPU: Piledriver, Family 15h (10h-1Fh)
- GPU: HD 8000D, TeraScale 3 "Devastator" (VLIW4), UVD 3.0, VCE 1.0
Speichercontroller: Dual Channel DDR3, bis DDR3-2133, unlocked bis DDR3-2400
CPU-PCIe: 24x PCIe 2.0 (davon 4 für den Chipsatz reserviert)
Chipsatz-Anbindung: 4x PCIe 2.0 (UMI)
Hardwarelux Test:
Test: AMD A10-6800K und A10-6700 - Hardwareluxx
Pünktlich zur Computex 2013 entließ AMD seine neuen APUs auf Richland-Basis in den Handel. Wie sie die neuen Modelle im Benchmark-Test schlagen, klärt dieser Test.www.hardwareluxx.de
CPU Modell Modules (Threads) CPU-Takt (Turbo) L2 Cache GPU Modell SP (SE/TE/ROPs) GPU-Takt TDP Marktstart RAM Sempron X2 250 1 (2) 3,2 (3,6) GHz 1MB deaktiviert 65 W DDR3-1866 Athlon X2 350 1 (2) 3,5 (3,9) GHz 1MB deaktiviert 65 W DDR3-1866 Athlon X2 370K 1 (2) 4,0 (4,2) GHz 1MB deaktiviert 65 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4 750 2 (4) 3,4 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB deaktiviert 65 W 10/2013 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4 760K 2 (4) 3,8 (4,1) GHz 2× 2MB deaktiviert 100 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 Athlon FX 670K 2 (4) 3,7 (4,3) GHz 2× 2MB deaktiviert 65 W 3/2014 DDR3-1866 A4-4000 1 (2) 3,0 (3,2) GHz 1MB HD 7480D 128 (32x4D/8/8) 720 MHz 65 W Q2/2013 DDR3-1333 A4-4020 1 (2) 3,2 (3,4) GHz 1MB HD 7480D 128 (32x4D/8/8) 720 MHz 65 W Q1/2014 DDR3-1333 A4-6300 1 (2) 3,7 (3,9) GHz 1MB HD 8370D 128 (32x4D/8/8) 760 MHz 65 W 06/2013 DDR3-1600 A4-6300B 1 (2) 3,7 (3,9) GHz 1MB HD 8370D 128 (32x4D/8/8) 760 MHz 65 W 06/2013 (OEM) DDR3-1600 A4-6320 1 (2) 3,8 (4,0) GHz 1MB HD 8370D 128 (32x4D/8/8) 760 MHz 65 W 12/2013 DDR3-1600 A4-6320B 1 (2) 3,8 (4,0) GHz 1MB HD 8370D 128 (32x4D/8/8) 760 MHz 65 W 03/2014 (OEM) DDR3-1600 A4-7300 1 (2) 3,8 (4,0) GHz 1MB HD 8470D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 800 MHz 65 W 8/2014 DDR3-1600 Pro A4-7300B 1 (2) 3,8 (4,0) GHz 1MB HD 8470D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 800 MHz 65 W 8/2014 (OEM) DDR3-1600 A6-6400B 1 (2) 3,9 (4,1) GHz 1MB HD 8470D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 800 MHz 65 W 6/2013 (OEM) DDR3-1866 A6-6400K 1 (2) 3,9 (4,1) GHz 1MB HD 8470D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 800 MHz 65 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 A6-6420B 1 (2) 4,0 (4,2) GHz 1MB HD 8470D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 800 MHz 65 W 1/2014 (OEM) DDR3-1866 A6-6420K 1 (2) 4,0 (4,2) GHz 1MB HD 8470D 192 (48x4D/12/8) 800 MHz 65 W 1/2014 DDR3-1866 A8-6500T 2 (4) 2,1 (3,1) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8550D 256 (64x4D/16/8) 720 MHz 45 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 A8-6500 2 (4) 3,5 (4,1) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8570D 256 (64x4D/16/8) 844 MHz 65 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 A8-6500B 2 (4) 3,5 (4,1) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8570D 256 (64x4D/16/8) 844 MHz 65 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 A8-6600K 2 (4) 3,9 (4,2) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8570D 256 (64x4D/16/8) 844 MHz 100 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 A10-6700T 2 (4) 2,5 (3,5) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8650D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 720 MHz 45 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 A10-6700 2 (4) 3,7 (4,3) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8670D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 844 MHz 65 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 A10-6790B 2 (4) 4,0 (4,3) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8670D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 844 MHz 100 W 10/2013 (OEM) DDR3-1866 A10-6790K 2 (4) 4,0 (4,3) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8670D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 844 MHz 100 W 6/2013 DDR3-1866 A10-6800B 2 (4) 4,1 (4,4) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8670D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 844 MHz 100 W 6/2013 (OEM) DDR3-2133 A10-6800K 2 (4) 4,1 (4,4) GHz 2× 2MB HD 8670D 384 (96x4D/24/8) 844 MHz 100 W 6/2013 DDR3-2133
Chipsätze:
- FM2: Hudson (A45, A55, A75, A85X)
- FM2+: Bolton (A58, A68H, A78, A88X)
3. FM2+
Fertigung: 28nm HKMG Bulk @ GF (28SHP)
Typ: APU
Architektur
- CPU: Steamroller, Family 15h (30h-3Fh)
- GPU: Radeon R5/R7, GCN 1.1 "Spectre", UVD 4.0, VCE 2.0
Speichercontroller: Dual Channel DDR3, bis DDR3-2133, unlocked bis DDR3-2400
CPU-PCIe: 16x PCIe 3.0 + 8x PCIe 2.0 (davon 4 für den Chipsatz reserviert)
Chipsatz-Anbindung: 4x PCIe 2.0 (UMI)
Hardwareluxx Test:
AMD A10-7800 unter die Lupe genommen - Hardwareluxx
Hardwareluxx hat den neuen AMD A10-7800 durch seinen Benchmark-Parcours geschickt und die taufrische Kaveri-APU gegen andere Modelle gegenübergestellt.www.hardwareluxx.de
AMDs Kaveri im Dual-Graphics-Test - Hardwareluxx
Hardwareluxx hat die Kaveri-Grafiklösung mit einer Radeon R7 250 im Dual-Graphics-Modus gekoppelt.www.hardwareluxx.de
Modellnummer Modules (Threads) Takt (max. Turbo) L2-Cache Multi GPU-Modell GPU-Konfiguration
ALUs (SE/TE/ROPs)GPU-Takt (Turbo) TDP Marktstart RAM Athlon X2 450 1 (2) 3,5 (3,9) GHz 1MB 35 deaktiviert 65 W 6/2014 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4 840 2 (4) 3,1 (3,8) GHz 2× 2MB 31 deaktiviert 65 W 8/2014 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4 860K 2 (4) 3,7 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB offen deaktiviert 95 W 8/2014 DDR3-2133 A6-7400K 1 (2) 3,5 (3,9) GHz 1MB offen R5 Spectre 256 (16×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 756 MHz 65 W 6/2014 DDR3-1866 A8-7500 2 (4) 3,0 (3,7) GHz 2× 2MB 30 R7 Spectre 384 (24×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 720 MHz 65 W unreleased DDR3-2133 A8-7600 2 (4) 3,1 (3,8) GHz 2× 2MB 31 R7 Spectre 384 (24×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 720 MHz 65 W 6/2014 DDR3-2133 A8-7650K 2 (4) 3,3 (3,8) GHz 2× 2MB offen R7 Spectre 384 (24×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 720 MHz 95 W 1/2014 DDR3-2133 A10-7700K 2 (4) 3,4 (3,8) GHz 2× 2MB offen R7 Spectre 384 (24×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 720 MHz 95 W 1/2014 DDR3-2133 A10-7800 2 (4) 3,5 (3,9) GHz 2× 2MB 35 R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 720 MHz 65 W 6/2014 DDR3-2133 A10-7850K 2 (4) 3,7 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB offen R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 720 MHz 95 W 1/2014 DDR3-2133 FX 770K 2 (4) 3,5 (3,9) GHz 2× 2MB offen deaktiviert 65 W 12/2014 (OEM) DDR3-2133 Pro A4-7350B 1 (2) 3,4 (3,8) GHz 1MB offen R5 Spectre 192 (12×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 514 MHz 65 W 6/2014 (OEM) DDR3-1866 Pro A6-7400B 1 (2) 3,5 (3,9) GHz 1MB 35 R5 Spectre 256 (16×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 756 MHz 65 W 6/2014 (OEM) DDR3-1866 Pro A8-7600B 2 (4) 3,1 (3,8) GHz 2× 2MB 31 R7 Spectre 384 (24×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 720 MHz 65 W 6/2014 (OEM) DDR3-2133 Pro A10-7800B 2 (4) 3,5 (3,9) GHz 2× 2MB 35 R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 720 MHz 65 W 6/2014 (OEM) DDR3-2133 Pro A10-7850B 2 (4) 3,7 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB 37 R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 720 MHz 95 W 6/2014 (OEM) DDR3-2133
Chipsätze:
- FM2+: Bolton (A58, A68H, A78, A88X)Fertigung: 28nm HKMG Bulk @ GF (28SHP)
Typ: APU
Architektur
- CPU: Steamroller, Family 15h (30h-3Fh)
- GPU: Radeon R5/R7, GCN 1.1 "Spectre", UVD 4.0, VCE 2.0
Speichercontroller: Dual Channel DDR3, bis DDR3-2133, unlocked bis DDR3-2400
CPU-PCIe: 16x PCIe 3.0 + 8x PCIe 2.0 (davon 4 für den Chipsatz reserveriert)
Chipsatz-Anbindung: 4x PCIe 2.0 (UMI)
Tests & Reviews:
AMD A10-8750 & DDR3-2133 - Grafikleistung im Test (by strikeeagle1977)
AMD A10-7890K & A8-7680 Vergleichstest (micha182)
Modellnummer Modules (Threads) Takt (max. Turbo) L2-Cache Multi GPU-Modell GPU-Konfiguration
ALUs (SE/TE/ROPs)GPU-Takt (Turbo) TDP Marktstart RAM Athlon X4 830 2 (4) 3,0 (3,4) GHz 2× 2MB 30 deaktiviert 65 W Q1/2018 DDR3-1866 Athlon X4 850 2 (4) 3,2 GHz 2× 2MB 32 deaktiviert 65 W Q2/2015 DDR3-2133 Athlon X4 870K 2 (4) 3,9 (4,1) GHz 2× 2MB offen deaktiviert 95 W 12/2015 DDR3-2133 Athlon X4 880K 2 (4) 4,0 (4,2) GHz 2× 2MB offen deaktiviert 95 W 1/2016 DDR3-2133 A6-7470K 1 (2) 3,7 (4,0) GHz 1MB offen R5 Spectre 256 (16×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 800 MHz 65 W 06/2016 DDR3-1866 A8-7670K 2 (4) 3,6 (3,9) GHz 2× 2MB offen R7 Spectre 384 (24×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 757 MHz 95 W 06/2015 DDR3-2133 A10-7860K 2 (4) 3,6 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB offen R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 757 MHz 95 W 2/2016 DDR3-2133 A10-7870K 2 (4) 3,9 (4,1) GHz 2× 2MB offen R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 866 MHz 95 W 5/2015 DDR3-2133 A10-7890K 2 (4) 4,1 (4,3) GHz 2× 2MB offen R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 866 MHz 95 W 3/2016 DDR3-2133 Pro A6-8550B 1 (2) 3,7 (4,0) GHz 1MB 37 R5 Spectre 256 (16×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 800 MHz 65 W 9/2015 (OEM) DDR3-1866 Pro A8-8650B 2 (4) 3,2 (3,9) GHz 2× 2MB 32 R7 Spectre 384 (24×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 757 MHz 65 W 9/2015 (OEM) DDR3-2133 Pro A10-8750B 2 (4) 3,6 (4,0) GHz 2× 2MB 36 R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 757 MHz 65 W 9/2015 (OEM) DDR3-2133 Pro A10-8850B 2 (4) 3,9 (4,1) GHz 2× 2MB 39 R7 Spectre 512 (32×Vec16-SIMD/32/8) 800 MHz 95 W 9/2015 (OEM) DDR3-2133
Chipsätze:
- FM2+: Bolton (A58, A68H, A78, A88X)Fertigung: 28nm HKMG Bulk @ GF (28SHP)
Typ: APU
Architektur
- CPU: Excavator, Family 15h (60h-6Fh)
- GPU: Radeon R5/R7, GCN 1.2, UVD 6.0, VCE 3.1
Speichercontroller: Dual Channel, bis DDR3-2400
CPU-PCIe: 8x PCIe 3.0 + 8x PCIe 2.0 (davon 4 für den Chipsatz reserveriert)
Chipsatz-Anbindung: 4x PCIe 2.0 (UMI)
Test & Reviews:
AMD A10-7890K & A8-7680 Vergleichstest (micha182)
Modellnummer Modules (Threads) Takt (max. Turbo) L2-Cache Multi GPU-Modell GPU-Konfiguration GPU-Takt (Turbo) TDP Marktstart RAM Athlon X4 835 2 (4) 3,1 (???) GHz 2× 1MB 31 deaktiviert 65 W DDR3-2133 Athlon X4 845 2 (4) 3,5 (3,8) GHz 2× 1MB 35 deaktiviert 65 W 02/2016 DDR3-2133 A6-7480 1 (2) 3,5 (3,8) GHz 1MB 35 Radeon R5 256 (16×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 900 65 W 10/2018 DDR3-2133 A8-7680 2 (4) 3,5 (3,8) GHz 2x 1MB 35 Radeon R7 384 (24×Vec16-SIMD/24/8) 900 65 W 10/2018 DDR3-2133
Chipsätze:
- FM2+: Bolton (offiziell nur A68H)
- Achtung: CPU-Kompatibilität des Mainboards beachten!
Overclocking (allgemein/spezifisch)
Unser alter OC Sammelthread:

 www.hardwareluxx.de
www.hardwareluxx.de
Allgemeines
- [BCLK OC] der interne Taktgeber ist nur bis 136MHz spezifiziert (und relativ ungenau)
- [BCLK OC] erfordert es den SATA Controller im IDE / Legacy Mode zu betreiben
- [BCLK OC] für hohe Frequenzen entweder den DVI-Anschluss der integrierten Grafik oder eine dGPU verwenden
- [BCLK OC] Übersicht der Modelle mit externem Taktgeber
- [RAM] es gibt nur 5 tRFC Stufen (90/110/160/300/350), liegt das Limit eures RAMs zwischen zwei Werten muss aufgerundet werden
- [RAM] Vorsicht mit der Vdimm, es gibt diverse Berichte von degradeten CPUs durch Spannungen über 1.65V/1.7V
- [RAM] einige Timings können je nach RAM fast beliebig reduziert werden, jedoch sind geringere Werte nicht immer schneller
- [RAM] die tREFI ist AMD typisch nicht konfigurierbar
- [iGFX] die Frequenz lässt sich bei einigen Mainboards frei in 1MHz Schritten einstellen, tatsächlich gibt es jedoch durch Teiler vorgegebene Takt-Stufen (BCLK-abhängig)
Llano (FM1)
2) Gigabyte A55 OC Guide @ HWBOT (PDF-Download)
3) Gigabyte A75 OC Guide @ HWBOT (PDF-Download)
Trinity & Richland (FM2)
2) AMD A10-5800K & Gigabyte F2A85X-UP4 - OC Guide @ PCGH
3) Gigabyte Trinity OC Guide @ Gigabyte Blog
Kaveri / Godavari / Carrizo (FM2+)
2) AMD A10-7850K & Gigabyte F2A88XN-WIFI - OC Guide @ Jagat Review

[Sammelthread] - AMD Llano / Trinity / Richland / Kaveri APU OC-Thread (OC-Listen, Links, FAQ)
AMD APU Overclocking de LUXX 1) Einleitung Dies soll die neue Anlaufstelle im Forum werden für alle Ergebnisse, Fragen und Diskussionen rund um das Thema Overclocking der AMD Llano (FM1) und Trinity (FM2) APUs. Da eine APU neben ihren CPU-Kernen auch noch GPU-Kerne besitzt, sollen hier auch...
Allgemeines
- [BCLK OC] der interne Taktgeber ist nur bis 136MHz spezifiziert (und relativ ungenau)
- [BCLK OC] erfordert es den SATA Controller im IDE / Legacy Mode zu betreiben
- [BCLK OC] für hohe Frequenzen entweder den DVI-Anschluss der integrierten Grafik oder eine dGPU verwenden
- [BCLK OC] Übersicht der Modelle mit externem Taktgeber
| FM1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ASRock | ASUS | Biostar | diverse |
| A75 Pro4-M (ICS 9LPRS477CKL) A75 Pro4 (ICS 9LPRS477CKL) A75 Pro4/MVP (ICS 9LPRS477CKL) A75 Extreme6 (ICS 9LPRS477CKL) | F1A55-M LE (ICS 9LPRS483AGLF / Handbuch) F1A55-M LE R2.0 (ICS 9LPRS483AGLF / Handbuch) F1A55-M (ICS 9LPRS483AGLF) F1A55 (ICS 9LPRS483AGLF / Handbuch) F1A55 R2.0 (ICS 9LPRS483AGLF / Handbuch) F1A55-V (ICS 9LPRS483AGLF / Handbuch) F1A75-M LE (ICS 9LPRS483AGLF / Handbuch) F1A75-M (ICS 9LPRS483BGLF / Handbuch) F1A75-V (ICS 9LPRS483AGLF / Handbuch) F1A75-M Pro (ICS 9LPRS477DKL / Handbuch) F1A75-M Pro R2.0 (ICS 9LPRS477DKL / Handbuch) F1A75-V Pro (ICS 9LPRS477DKL) F1A75-V Evo (ICS 9LPRS477DKL / Handbuch) | TA75M+ (Realtek RTM880N-793, 2) TA75A+ (Realtek RTM880N-793, 2) | Colorful Battle-AX C.A75 X5 (]ICS 9LPRS471CKL, 2) Colorful Battle-AX C.A75 X5 V14 (ICS 9LPRS471CKL) ECS Black A75F-A Deluxe (ICS 9LPRS471CKL, 2) Onda A75 (nur erste Revision?) Unika UA55GT EVO (ICS ...?) Unika TAC75 Ultra3 (Realtek RTM880N-790) Unika UA75GT EVO (Realtek RTM880N-790) |
| Gigabyte | Maxsun | Sapphire | Soyo |
| A55M-S2V (ICS 9LPRS477DKL, 2) A55M-DS2 (Realtek RTM880T-792) A75M-S2V (ICS 9LPRS477DKL) A55-DS3P (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) A75M-D2H (ICS 9LPRS477DKL) A75M-UD2H (ICS 9LPRS477DKL) A75-D3H (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) A75-UD4H (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) | Maxsun MS-A55M Pro (Realtek RTM880N-790) Maxsun MS-A55A (ICS 9LPRS471CKL) Maxsun MS-A75MU3 Pro (ICS 9LPRS471CKL, 2) Maxsun MS-A75UD3 Pro (Realtek RTM880N-790, 2) | Pure Platinum A75V Pure Platinum A75P (ICS 9VRS4818AKLF) Pure Platinum A75 (ICS 9VRS4818AKLF) | Soyo SY-A55M+ (Realtek RTM880N-790) Soyo SY-A55A-GR (Realtek RTM880N) Soyo SY-A75M+ (ICS 9LPRS471CKL) Soyo SY-A75+ (ICS 9LPRS471CKL) |
| FM2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ASRock | ASUS | Biostar | diverse |
| FM2A75 Pro4-M (nur ES!) FM2A75 Pro4 (nur ES!) | F2A85-M Pro (ICS 9LPRS477DKL / Fotos) F2A85-V Pro (ICS 9LPRS477DKL) | Hi-Fi A85S (Realtek RTM880N-793) Hi-Fi A85W (Realtek RTM880N-793, [2]) Hi-Fi A85X (Realtek RTM880N-793) | Colorful Battle-AX C.A75K V15 (Realtek RTM880N-790) Jetway / Unika HA20-85X (Realtek RTM880n-790) Jetway/ Unika HA21-85X (Realtek RTM880N-790) |
| ECS | Gigabyte | MSI | Sapphire |
| A75F2-A2 (ICS ...) Black A85F2-A Golden (ICS 9LPRS477DKL) Black A85F2-A Deluxe | A85X-D3H (AMD ES, ICS 9LRS4850AKL) F2A85X-UP4 (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) | FM2-A55-G43 FM2-A75MA-E35 (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) FM2-A85XMA-E35 (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) FM2-A85XA-G43 FM2-A85X-G65 (ICS 9LRS4850AKL, [2]) | Pure Platinum A85XT (ICS 9VRS4818AKLF, 2) |
| FM2+ | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ASUS | Biostar | Gigabyte | [td]MSI |
| A88XM-Pro (ES) A88X-Pro (ICS 9LPRS477DKL, 2) ROG Crossblade Ranger (ICS 9LPRS477DKL, [2]) | Hi-Fi A88W (Realtek RTM880N-793) | F2A88X-UP4 (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) | A88XM Gaming (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) A88X-G43 A88X-G45 Gaming (ICS 9LRS4850AKL) |
- [RAM] Vorsicht mit der Vdimm, es gibt diverse Berichte von degradeten CPUs durch Spannungen über 1.65V/1.7V
- [RAM] einige Timings können je nach RAM fast beliebig reduziert werden, jedoch sind geringere Werte nicht immer schneller
- [RAM] die tREFI ist AMD typisch nicht konfigurierbar
- [iGFX] die Frequenz lässt sich bei einigen Mainboards frei in 1MHz Schritten einstellen, tatsächlich gibt es jedoch durch Teiler vorgegebene Takt-Stufen (BCLK-abhängig)
Llano (FM1)
Referenztakt (BCLK): integrierter Taktgeber bis mindestens 136MHz, mit externem Taktgeber auf dem Mainboard bis über 170MHz
CPU-Takt: als Multiplikator, unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
NB-Takt: als Multiplikator, unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
iGFX: unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
RAM: nativ von DDR3-1066 bis DDR3-1866, höhere Taktraten durch BCLK-OC
The Stilt schrieb:The northbridge clock (NCLK) can be indeed adjusted by dividers ranging from 2 to 15.75 (/MainPLL).
However there is a rule which limits the maximum NCLK frequency: NCLK must always be less or equal than the memory frequency (MEMCLK). Also not all of the NCLK dividers are considered desireable. They do work, but there is a minor hit in memory write performance. The "undesireable" dividers are the reason why the "clock to clock" performance is worse on certain dividers. Not because of these dividers are used, but because they are not used.
Source: http://www.xtremesystems.org/forums...U-vantage-wr&p=4922861&viewfull=1#post4922861
1) AMD Llano OC Guide @ Corsair ForumSF3D schrieb:Here is explanation for IGP clocks.
MainPLL (3600MHz) / GPU divider (default 6) = GPU clocks (default 600)
BCLK 150 = MainPLL (5400) / GPU divider 5 = GPU clocks 1080MHz
Source: http://www.xtremesystems.org/forums...U-vantage-wr&p=4915849&viewfull=1#post4915849
2) Gigabyte A55 OC Guide @ HWBOT (PDF-Download)
3) Gigabyte A75 OC Guide @ HWBOT (PDF-Download)
Trinity & Richland (FM2)
1) AMD Trinity OC Guide (ASRock) @ OC InsideReferenztakt (BCLK): integrierter Taktgeber bis mindestens 136MHz, mit externem Taktgeber auf dem Mainboard bis über 170MHz
CPU-Takt: als Multiplikator, unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
NB-Takt: als Multiplikator, unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
iGFX: unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
RAM: nativ von DDR3-1066 bis DDR3-2400, höhere Taktraten durch BCLK-OC

2) AMD A10-5800K & Gigabyte F2A85X-UP4 - OC Guide @ PCGH
3) Gigabyte Trinity OC Guide @ Gigabyte Blog
Kaveri / Godavari / Carrizo (FM2+)
1) ASUS Crossblade Ranger OC Guide @ ASUS ROGReferenztakt (BCLK): integrierter Taktgeber bis mindestens 136MHz, mit externem Taktgeber auf dem Mainboard bis über 170MHz
CPU-Takt: als Multiplikator, unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
NB-Takt: als Multiplikator, unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
iGFX: unlocked bei Black Editions bzw K-Modellen, sonst nur OC per BCLK
RAM: nativ von DDR3-1066 bis DDR3-2400, höhere Taktraten durch BCLK-OC
2) AMD A10-7850K & Gigabyte F2A88XN-WIFI - OC Guide @ Jagat Review
Anhang 1) - Nützliches im WWW
1) Übersicht aller AMD APUs @ Wikipedia
2) Spezifikationen aller AMD Prozessoren @ AMD
3) Wikichip Plattform-Spezifikationen: FM1 | FM2 | FM2+
4) Retro-Reviews bei Planet3dnow: AMD A8-3870K | A10-6800K
5) Retro-Review bei Igor's Labs: AMD A10-7890K
6) Prozessor-Übersicht mit vielen Sondermodellen (einige davon werde ich hier noch nachtragen): e-junkie.de
2) Spezifikationen aller AMD Prozessoren @ AMD
3) Wikichip Plattform-Spezifikationen: FM1 | FM2 | FM2+
4) Retro-Reviews bei Planet3dnow: AMD A8-3870K | A10-6800K
5) Retro-Review bei Igor's Labs: AMD A10-7890K
6) Prozessor-Übersicht mit vielen Sondermodellen (einige davon werde ich hier noch nachtragen): e-junkie.de
Anhang 2) - Downloads
OC-Tools
1) AMD PSCheck 3.4.1 @ Overclockers.com (direkter Download)
2) AMDMsrTweaker @ GitHub & Linux Port @ Github
3) Die APU OC Tools von The_Stilt @ HWBOT
4) K15tk - Kaveri Overclocking Utility @
5) AMD Overdrive Utility @ Computerbase
6) K10stat (für Llano) @ Google Software
7) CPU-Z vor V2.00 zeigen die Speichertimings im Gegensatz zu neueren Versionen korrekt an (Download V1.88 (Zip))
Modifizierte BIOSe
1) ASRock/ASUS/Gigabyte/MSI Mod BIOSe mit deaktiviertem GeAPM (The_Stilt): Overclock.net
Grafik-Treiber:
1) Llano (A4/A8-3xxx) @ AMD
2) Trinity (A4/A10-5xxx) @ AMD
3) Richland (A4/A10-6xxx) @ AMD
4) Kaveri/Godavari (A4/A10-7xxx/8xxx) @ AMD (WinXP)
5) Carrizo (A4/A12-8xxx) @ AMD
Chipsatz-Treiber:
1) AMD PSCheck 3.4.1 @ Overclockers.com (direkter Download)
2) AMDMsrTweaker @ GitHub & Linux Port @ Github
3) Die APU OC Tools von The_Stilt @ HWBOT
4) K15tk - Kaveri Overclocking Utility @
5) AMD Overdrive Utility @ Computerbase
6) K10stat (für Llano) @ Google Software
7) CPU-Z vor V2.00 zeigen die Speichertimings im Gegensatz zu neueren Versionen korrekt an (Download V1.88 (Zip))
Modifizierte BIOSe
1) ASRock/ASUS/Gigabyte/MSI Mod BIOSe mit deaktiviertem GeAPM (The_Stilt): Overclock.net
Grafik-Treiber:
1) Llano (A4/A8-3xxx) @ AMD
2) Trinity (A4/A10-5xxx) @ AMD
3) Richland (A4/A10-6xxx) @ AMD
4) Kaveri/Godavari (A4/A10-7xxx/8xxx) @ AMD (WinXP)
5) Carrizo (A4/A12-8xxx) @ AMD
Chipsatz-Treiber:
AMD bietet dieses nicht mehr direkt zum Download an. Treiber müssen also über die Support-Seiten eines Mainboard-Herstellers oder von einem OEM heruntergeladen werden.
Zum Beispiel
1) ASRock Llano @ v8.947 WinXP32/64 (direkter Download) | v12.8 WinVista/7/8 (direkter Download) | v13.15.102 Win8.1 (direkter Download)
2) MSI Trinity/Richland v9.00.100.2 @ WinXP32 (direkter Download)
3) Gigabyte Kaveri v9.00.300.304 @ WinXP32 (direkter Download)
4) ASUS Trinity/Richland/Kaveri AllinOne Repack @ WinXP32 (direkter Download) | Win10 (direkter Download)
5) Biostar FM2/FM2+ AllinOne Repack v15.200.1065 @ Win7/8/8.1/10 (direkter Download)
6) FM2+ Kaveri/Godavari/Carrizo v18.30.18 Win10/Win7 @ MSI (direkter Download)
Anhang 3) - Dual Graphics
1) Llano
2) Trinity
3) Richland (Quelle: AMD)
3) Kaveri (Quelle: AMD)
Dual Graphics FAQ @ AMD:
Dual Graphics Übersicht @ CPU-World:
- HD 6350 - A4 Series
- HD 6450 - A8, A6 & A4 Series
- HD 6570 - A8 & A6 Series
- HD 6670 - A8 & A6 Series
- HD 7350 - A4 Series
- HD 7450 - A8, A6 & A4 Series
- HD 7570 - A8 & A6 Series
- HD 7670 - A8 & A6 Series

2) Trinity
- HD 6450 - AMD A6 Series
- HD 6570 (Turks Pro) - AMD A10 & A8 Series
- HD 6670 (Turks XT) - AMD A10 Series
- HD 7450 - A6 Series
- HD 7470 - A10, A8 & A6 Series
- HD 7570 - A10, A8 & A6 Series
- HD 7670 - A10, A8 & A6 Series
- FirePro V3900/V4900 (Turks GL, Turks XT GL) - FirePro A320 & A300 (Quelle: e_junie)
- HD 7750 - A10 Series & ??? (Quelle: TechPowerUp)

3) Richland (Quelle: AMD)
- HD 6450 - AMD A6-6400K / A6-6420K
- HD 6570 - AMD A10-6800K / A10-6790K / A8-6600K / AMD A6-6400K / A6-6420K
- HD 6670 - AMD A10-6800K / A10-6790K / A8-6600K
- HD 7750 - A10 Series & ??? (Quelle: HWBOT & HWBOT-2, ggf Treiberabhängig)

![AMD Dual Graphics Kaveri - Simple Table [2].png AMD Dual Graphics Kaveri - Simple Table [2].png](https://www.hardwareluxx.de/community/data/attachments/723/723589-7694a1a97b6f94870b43e3d6be9c87b9.jpg)
3) Kaveri (Quelle: AMD)
- Radeon R5 230 “Oland LE”
- Radeon R7 240 “Oland Pro”
- Radeon R7 250 “Oland XT”
- Radeon HD 8570 OEM “Oland XT”
- Radeon HD 8670 OEM “Oland XT”
- Radeon HD 7730 “Cape Verde LE”
- Radeon HD 7750 “Cape Verde Pro”
- Radeon R7 255 OEM “Cape Verde Pro”

![AMD Dual Graphics Kaveri - Simple Table [2].png AMD Dual Graphics Kaveri - Simple Table [2].png](https://www.hardwareluxx.de/community/data/attachments/723/723589-7694a1a97b6f94870b43e3d6be9c87b9.jpg)


Kaver Dual Graphics Performance:
AMDs Kaveri im Dual-Graphics-Test - Hardwareluxx
Hardwareluxx hat die Kaveri-Grafiklösung mit einer Radeon R7 250 im Dual-Graphics-Modus gekoppelt. www.hardwareluxx.de
www.hardwareluxx.de

AMD Kaveri: Hersteller-Benchmarks zu "Dual Graphics"-Lösungen mit R7 240/250 veröffentlicht
Der kalifornische Chiphersteller AMD hebt neben Frame-Pacing-, HSA- und Mantle-Funktionen auch "Dual Graphics"-Kompatibilität mit den hauseigenen Kaveri-APUs beim aktuellsten Beta-Treiber hervor. Dabei werden explizit die Radeon R7 250 sowie R7 240 in den DDR3-Versionen genannt, zu denen AMD...www.pcgameshardware.de
Dual Graphics FAQ @ AMD:
Q1: What is AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A1: AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics is an innovative technology exclusive to AMD platforms that allows AMD APUs and select AMD Radeon™ discrete graphics cards to work together. When combined, the platform delivers stunning high definition and DirectX® 11.2 and DirectX® 10 capabilities that are better than either device alone. Currently, AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics is supported on the AMD A-Series APUs in conjunction with select AMD Radeon™ R7 series and AMD Radeon™ HD 6000 series graphics cards used under the Microsoft Windows 7 operating system.
Q2: How do I know my AMD Radeon™ HD Graphics card is capable of supporting AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A2: Go to http://www.amd.com/dualgraphics and review the Notebook and Desktop tabs to see the recommended discrete graphics card pairings for your APU.
Q3: I just bought an AMD Radeon™ R7 series graphics card. How do I configure my PC to take advantage of AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A3: To take advantage of AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics, you must use a compatible AMD A-Series APU to pair with your supported AMD Radeon™ R7 series card. After installation of your graphics card, visit the AMD Graphics Drivers and Software Page, to download andinstall the latest AMD graphics drivers. After driver installation, the option to enable AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics should become available in the AMD Catalyst Control Center.
Once installed, go into the “Performance” section of the AMD Catalyst Control Center and check the box that says “Enable Crossfire™.” This will allow the AMD A-Series APU graphics to work in tandem with the select AMD Radeon™ R7 series GPU installed for increased graphics performance.
Q4: Where do I plug my monitor in to get the best performance when using AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics technology?
A4: For best performance, AMD recommends plugging the display into your discrete graphics card. This will ensure that even applications that do not take advantage of AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics will still be able to run on the faster graphics card in your system. However, to be more accurate, we recommend that you plug your monitor into the AMD Radeon™ graphics with the higher model number. If that is your APU, plug into the motherboard, if it is your discrete graphics card, plug into that.
Q5: Why doesn’t my DirectX® 9 game look better on AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A5: AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics was designed only for the latest DirectX® levels to allow AMD to focus resources on providing an optimal user experience on the latest graphics technologies. AMD encourages users to take advantage of these and numerous other innovations that have come to market recently by upgrading system hardware.
AMD Radeon™ HD R7 series graphics, found in both AMD A-Series APUs and discrete video cards, are designed to deliver the best possible DirectX® 11.2 experience. As such, the dual graphics performance increase is applicable to select DirectX® 11.2- and DirectX® 10-enabled applications. For DirectX® 9 applications, the combined performance will be disabled and the fastest graphics engine will perform those tasks; however, users will still experience the speed and performance of AMD Radeon™ graphics.
Q6: Does AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics work with AMD Eyefinity technology?
A6: AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics will support AMD Eyefinity technology as long as your discrete GPU supports AMD Eyefinity technology and monitors are plugged into the discrete GPU outputs.
Q7: With a multi-monitor setup, why do some of the displays become disabled when I enable AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A7: AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics is a form of AMD CrossFireX™ technology, and, with the current solution, only displays from the “master” graphics device (the one that monitors are plugged into) are available. The other displays are disabled. To ensure your displays remain available, make sure to connect your displays to the “master” graphics device. The “master” device settings can be found in the AMD Catalyst Control Center, which is the user interface for the drivers and installation package.
Additional hardware (e.g. HD or 4K monitor, USB, 3.0 ports, wirelessly enabled HDTV) and/or software (e.g. multimedia applications and/or Wi-Fi access) are required for the full enablement of some features. HD/4K Video display requires an HD/4K video source. Not all features may be supported on all components or systems - check with your component or system manufacturer for specific model capabilities and supported technologies.
Foot Notes (removed)
AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics requires an AMD “A” series APU plus an AMD Radeon™ discrete graphics configuration and is available on Windows® 7 Professional, Windows 7 Ultimate, Windows® 7 Home Premium, and/or Windows® 7 Home Basic OS. Linux OS supports manual switching which requires restart of X-Server to engage and/or disengage the discrete graphics processor for dual graphics capabilities. Additional hardware (e.g. Blu-ray drive, HD or 10-bit monitor, TV tuner, wirelessly enabled HDTV) and/or software (e.g. multimedia applications) are required for the full enablement of some features. HD Video display requires an HD video source. Not all features may be supported on all components or systems - check with your component or system manufacturer for specific model capabilities and supported technologies.
1) Boost visual performance up to 123% when you combine this AMD Quad-Core A8 APU with the AMD Radeon™ HD 6670 graphics card. Testing done in AMD Performance Labs using 3DMark Vantage – Performance Benchmark as a metric for visual performance, in the best of 3 runs. The AMD A8 APU-based system scored 4038 marks while the AMD A8 APU-based Dual Graphics system scored 9021 marks. All scores rounded to the nearest whole number. The AMD A8 APU-based system is represented by the reference design codename "Armorhead", consisting of the AMD Quad-Core A8-3850 APU with AMD Radeon™ HD 6550D Discrete Level Graphics, 8GB DDR3-1600 system memory, a Real SSD C300 hard drive (256G) and Microsoft Windows Ultimate 64-bit. The AMD A8 APU-based Dual Graphics system consists of the same hardware with the addition of an AMD Radeon™ HD 6670 discrete graphics card, creating an AMD Quad-Core A8-3850 APU with AMD Radeon™ HD 6690D2 Dual Graphics-based system. DT20112H-I3
2) AMD Eyefinity technology works with games that support non-standard aspect ratios, which is required for panning across multiple displays. To enable more than two displays, additional panels with native DisplayPort™ connectors, and/or DisplayPort™ compliant active adapters to convert your monitor’s native input to your card’s DisplayPort™ or Mini-DisplayPort™ connector(s), are required. SLS (Single Large Surface) functionality requires an identical display resolution on all configured displays.
*For more information on AMD features and software go to amd.com/featuredetails.
A1: AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics is an innovative technology exclusive to AMD platforms that allows AMD APUs and select AMD Radeon™ discrete graphics cards to work together. When combined, the platform delivers stunning high definition and DirectX® 11.2 and DirectX® 10 capabilities that are better than either device alone. Currently, AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics is supported on the AMD A-Series APUs in conjunction with select AMD Radeon™ R7 series and AMD Radeon™ HD 6000 series graphics cards used under the Microsoft Windows 7 operating system.
Q2: How do I know my AMD Radeon™ HD Graphics card is capable of supporting AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A2: Go to http://www.amd.com/dualgraphics and review the Notebook and Desktop tabs to see the recommended discrete graphics card pairings for your APU.
Q3: I just bought an AMD Radeon™ R7 series graphics card. How do I configure my PC to take advantage of AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A3: To take advantage of AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics, you must use a compatible AMD A-Series APU to pair with your supported AMD Radeon™ R7 series card. After installation of your graphics card, visit the AMD Graphics Drivers and Software Page, to download andinstall the latest AMD graphics drivers. After driver installation, the option to enable AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics should become available in the AMD Catalyst Control Center.
Once installed, go into the “Performance” section of the AMD Catalyst Control Center and check the box that says “Enable Crossfire™.” This will allow the AMD A-Series APU graphics to work in tandem with the select AMD Radeon™ R7 series GPU installed for increased graphics performance.
Q4: Where do I plug my monitor in to get the best performance when using AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics technology?
A4: For best performance, AMD recommends plugging the display into your discrete graphics card. This will ensure that even applications that do not take advantage of AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics will still be able to run on the faster graphics card in your system. However, to be more accurate, we recommend that you plug your monitor into the AMD Radeon™ graphics with the higher model number. If that is your APU, plug into the motherboard, if it is your discrete graphics card, plug into that.
Q5: Why doesn’t my DirectX® 9 game look better on AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A5: AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics was designed only for the latest DirectX® levels to allow AMD to focus resources on providing an optimal user experience on the latest graphics technologies. AMD encourages users to take advantage of these and numerous other innovations that have come to market recently by upgrading system hardware.
AMD Radeon™ HD R7 series graphics, found in both AMD A-Series APUs and discrete video cards, are designed to deliver the best possible DirectX® 11.2 experience. As such, the dual graphics performance increase is applicable to select DirectX® 11.2- and DirectX® 10-enabled applications. For DirectX® 9 applications, the combined performance will be disabled and the fastest graphics engine will perform those tasks; however, users will still experience the speed and performance of AMD Radeon™ graphics.
Q6: Does AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics work with AMD Eyefinity technology?
A6: AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics will support AMD Eyefinity technology as long as your discrete GPU supports AMD Eyefinity technology and monitors are plugged into the discrete GPU outputs.
Q7: With a multi-monitor setup, why do some of the displays become disabled when I enable AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics?
A7: AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics is a form of AMD CrossFireX™ technology, and, with the current solution, only displays from the “master” graphics device (the one that monitors are plugged into) are available. The other displays are disabled. To ensure your displays remain available, make sure to connect your displays to the “master” graphics device. The “master” device settings can be found in the AMD Catalyst Control Center, which is the user interface for the drivers and installation package.
Additional hardware (e.g. HD or 4K monitor, USB, 3.0 ports, wirelessly enabled HDTV) and/or software (e.g. multimedia applications and/or Wi-Fi access) are required for the full enablement of some features. HD/4K Video display requires an HD/4K video source. Not all features may be supported on all components or systems - check with your component or system manufacturer for specific model capabilities and supported technologies.
Foot Notes (removed)
AMD Radeon™ Dual Graphics requires an AMD “A” series APU plus an AMD Radeon™ discrete graphics configuration and is available on Windows® 7 Professional, Windows 7 Ultimate, Windows® 7 Home Premium, and/or Windows® 7 Home Basic OS. Linux OS supports manual switching which requires restart of X-Server to engage and/or disengage the discrete graphics processor for dual graphics capabilities. Additional hardware (e.g. Blu-ray drive, HD or 10-bit monitor, TV tuner, wirelessly enabled HDTV) and/or software (e.g. multimedia applications) are required for the full enablement of some features. HD Video display requires an HD video source. Not all features may be supported on all components or systems - check with your component or system manufacturer for specific model capabilities and supported technologies.
1) Boost visual performance up to 123% when you combine this AMD Quad-Core A8 APU with the AMD Radeon™ HD 6670 graphics card. Testing done in AMD Performance Labs using 3DMark Vantage – Performance Benchmark as a metric for visual performance, in the best of 3 runs. The AMD A8 APU-based system scored 4038 marks while the AMD A8 APU-based Dual Graphics system scored 9021 marks. All scores rounded to the nearest whole number. The AMD A8 APU-based system is represented by the reference design codename "Armorhead", consisting of the AMD Quad-Core A8-3850 APU with AMD Radeon™ HD 6550D Discrete Level Graphics, 8GB DDR3-1600 system memory, a Real SSD C300 hard drive (256G) and Microsoft Windows Ultimate 64-bit. The AMD A8 APU-based Dual Graphics system consists of the same hardware with the addition of an AMD Radeon™ HD 6670 discrete graphics card, creating an AMD Quad-Core A8-3850 APU with AMD Radeon™ HD 6690D2 Dual Graphics-based system. DT20112H-I3
2) AMD Eyefinity technology works with games that support non-standard aspect ratios, which is required for panning across multiple displays. To enable more than two displays, additional panels with native DisplayPort™ connectors, and/or DisplayPort™ compliant active adapters to convert your monitor’s native input to your card’s DisplayPort™ or Mini-DisplayPort™ connector(s), are required. SLS (Single Large Surface) functionality requires an identical display resolution on all configured displays.
*For more information on AMD features and software go to amd.com/featuredetails.
Dual Graphics Übersicht @ CPU-World:
Anhang 4) - APUs & Single Rank vs Dual Rank Performance
Test bei Computerbase:

 www.computerbase.de
www.computerbase.de
Rank Interleaving gibt es nicht erst seit Kaveri. 2RpC spielen also auch schon für Llano, Trinity und Richland eine Rolle.
Hier ein Vergleich mit einem A8-3870K, A10-5800K, A10-6800K und A10-7850K:
Reiche ich später nach.

AMDs Kaveri und der Speicher: Viel Takt und „Dual Rank“ muss es sein
Nicht nur der Speichertakt spielt bei AMDs „Kaveri“ eine Rolle, auch die Anzahl und der Aufbau der verwendeten Module hat entscheidende Auswirkungen auf die Leistungsfähigkeit.
Rank Interleaving gibt es nicht erst seit Kaveri. 2RpC spielen also auch schon für Llano, Trinity und Richland eine Rolle.
Hier ein Vergleich mit einem A8-3870K, A10-5800K, A10-6800K und A10-7850K:
Reiche ich später nach.
Anhang 5) AM1 - Sockel FS1b (2014)
Die Plattform


 www.hardwareluxx.de
www.hardwareluxx.de

 www.anandtech.com
www.anandtech.com
Die Prozessoren (SOCs)
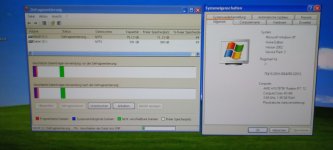
Die Mainboards (angekündigt zum Launch)
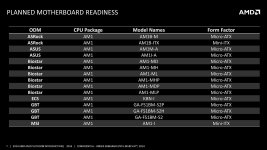
Launch Coverage

 www.computerbase.de
www.computerbase.de

 www.au-ja.de
www.au-ja.de

 www.anandtech.com
www.anandtech.com

 www.servethehome.com
www.servethehome.com
 www.phoronix.com
www.phoronix.com
AMDs AM1-Plattform geht offiziell an den Start - Hardwareluxx
AMDs AM1-Plattform ist nun offiziell.

AMD AM1 Platform Announced: Socketed Kabini
Die Prozessoren (SOCs)
| Boxed-Kühler AMD 1A213LQ00 | Athlon 5370 (Q1/2016) | Athlon 5350 (A6-5350) | Ahtlon 5150 (A4-5150) | Sempron 3850 (E2-3850) | Sempron 2650 (E1-2650) |
| Cores / Threads | 4 / 4 | 4 / 4 | 4 / 4 | 4 / 4 | 2 / 2 |
| CPU Frequency | 2200 | 2050 | 1600 | 1300 | 1450 |
| GPU | HD 8400 | HD 8400 | HD 8400 | HD 8280 | HD 8240 |
| GPU SPs | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 |
| GPU Frequency | 600 | 600 | 600 | 450 | 400 |
| L2 Cache | 2MB | 2MB | 2MB | 2MB | 1MB |
| TDP | 25 W | 25 W | 25 W | 25 W | 25 W |
Die Mainboards (angekündigt zum Launch)

Launch Coverage

AMD Athlon 5350 im Test: Der 8-Watt-Selbstbau-PC
AMDs „Kabini“ hat den Weg in den Desktop-PC gefunden. Wir testen das Flaggschiff Athlon 5350 mit der zugehörigen Plattform „AM1“ inklusive sparsamem 75-Watt-Netzteil.

Au-Ja! - ASUS AM1M-A - Sockel AM1 (Kabini) für Übertakter - 1/13
IT-Nachrichten, Tests und Berichte

AMD AM1 Kabini Part 2: Athlon 5350/5150 and Sempron 3850/2650 Tested

AMD Athlon 5350 Linux Benchmarks and Review
The AMD Athlon 5350 will be the highest performing AM1 processor at launch. It provides solid low power CPU performance for this segment and GCN based GPU
AMD Athlon 5350 APU On Linux (AM1 Platform) Review - Phoronix
emissary42 schrieb:Diesen Thread widme ich allen, die sich damals im Forum aktiv an den APU Sammelthreads und Übersichten beteiligt haben. Insbesondere Reous, Low, Pirate85, Bob_Busfahrer, Novma, Chaser84, e junkie und Rest unserer kleinen OC-Crew. Vielleicht kann dieser Thread andere dazu inspirieren, sich auch wieder aktiv(er) im Forum einzubringen und Inhalte für Themen zu erstellen, die euch selbst am Herzen liegen.
1) Sockelfotos einfügen -- erledigt (22.0.2.23)
2) PinMap für FM2+ auftreiben
3)Dual Graphics Konfigurationen vervollständigen -- offizielle Tabellen & AMD FAQ ergänzt (22.03.23)
4) Single vs Dual Rank vs Dual Rank ohne Rank Interleaving Benchmarks nachtragen
5)AM1-Infos ergänzen -- erledigt (16.03.24)
6) K15tk Download bereit stellen
2) PinMap für FM2+ auftreiben
3)
4) Single vs Dual Rank vs Dual Rank ohne Rank Interleaving Benchmarks nachtragen
5)
6) K15tk Download bereit stellen
Zuletzt bearbeitet: