@NetworkerZ
Asus sagt dazu:
The available memory under 32-bit Windows XP is 2GB only when I have 4GB memory installed and memory remap enabled in BIOS. When I disable memory function in BIOS, the available memory under 32-bit Windows XP becomes 2.93GB. How do I fix this?
<table bgcolor="#ffffff" border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="7" width="100%"><tbody><tr align="center" bgcolor="#ffffff"> <td colspan="4"> <table bgcolor="#fff5d7" border="0" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="0" width="100%"> <tbody><tr> <td width="75%">
Answer</td> </tr> </tbody></table> </td> </tr> <tr align="center" bgcolor="#ffffff"> <td colspan="4"> <table bgcolor="#fff5d7" border="0" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="1" width="100%"> <tbody><tr> <td align="center" bgcolor="#ffffff" valign="top"> <table border="0" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" width="100%"> <tbody><tr> <td class="faq_content" colspan="2" bgcolor="#ffffff" valign="top">This is a limitation of 32-bit Windows XP. When the memory remap function is enabled, the occupied memory address is remapped to above 4G. In addition, the remap is done in 1G block as an unit. Since the available memory is 2.93GB without remap, when remap is enabled, the memory address between 2-4GB is remapped to above 4G. However, 32-bit OS does not recognize anything above 4G. Consequently, the remapped 2GB is lost. The available memory address under 32-bit OS is reduced to 2G. Hence under 32-bit OS, it is recommended to keep remap function disabled.</td></tr></tbody></table></td></tr></tbody></table></td></tr></tbody></table>



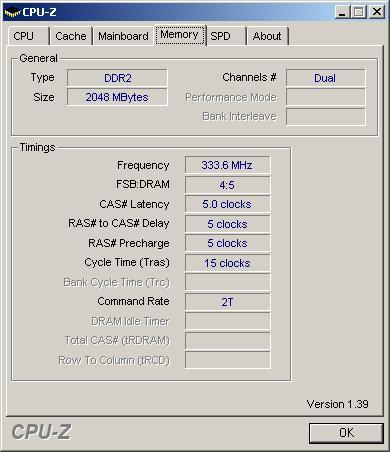
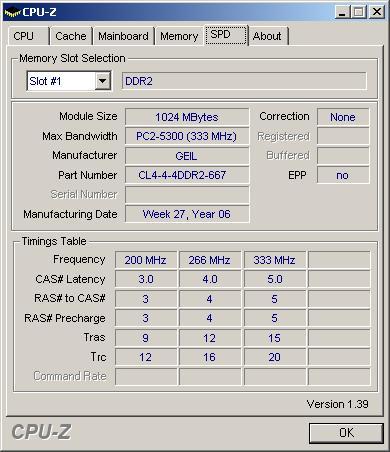





 wenns 100% Mehrleistung wären ok, aber für das bischen Mehrleistung geb ich nicht so viel Kohle aus
wenns 100% Mehrleistung wären ok, aber für das bischen Mehrleistung geb ich nicht so viel Kohle aus
 is da eher das Board schuld oder kann das auch vom RAM kommen? Google hilft dabei leider nicht viel - hab nur das gefunden
is da eher das Board schuld oder kann das auch vom RAM kommen? Google hilft dabei leider nicht viel - hab nur das gefunden